Along with the Basics in Java Programming Language, there are some Advanced Concepts that we have to learn to become Expert developers. “Throw an Exception in Java” is one such advanced concept.
Throwing Exceptions in Java helps ensure flawless program execution irrespective of the presence of an error. In this article, we will first discuss Exceptions in Java and their different types.
Later, we will discuss some practical implementation processes for throwing exceptions in Java. So, let us start our discussion.
Summary Or Key Highlights:
- Exception is an unexpected event that stops the Java Program Execution with an Error Message.
- When we throw an Exception in Java, we can execute and get the output even if there is an error.
- With 3 Different Methods, we can throw an Exception in Java Programming Language.
- There are some differences in exceptions between Java and Other Programming Languages.
- We can see the use of exceptions in Java from Web Development to Enterprise-Level Applications.
What Are Exceptions In Java? Read Below
We can say the Exception in Java is an unexpected event that stops the program execution. There might be different reasons to have exceptions in Java, like Invalid User Input, File Not Found, Division by zero, etc.
If there is any such exception, then the Java Compiler can mark it and stop the program execution during Compile-time or Runtime. To avoid such issues, we can Throw Exceptions in Java.
If the developer has an intuition that there can be an exception that will halt the program execution, then he can throw an Exception in Java. In that case, the program execution will not be stopped suddenly.
Historical Evolution Of Java Exceptions:
- 1990s: The Built-in Exception Handling processes like Try-Catch and THROW were introduced.
- 2000s: The Exception Handling gets improved with a focus on Checked vs. Unchecked Exceptions.
- 2010s: Multi-catch and Try-with-Resources were introduced to do more enhancements.
- 2020s: Further Optimizations are being done in the Java Exceptions to increase performance.
What Are Different Types Of Exceptions In Java?
After discussing the definition of the Java Exceptions, it is time to move ahead for some deeper concepts. Before starting the practical implementations, in this section, we will state the Different Types of Java Exceptions.
In Java, there are mainly two types of Exceptions that are highly used. These two exceptions belong to the Built-in Category. Let us check the following list to know more about them.
- Checked Exceptions: Checked Exceptions are also called as the Compile-time Exceptions because these are caught during the Compilation of the Java Program. Some of the Checked Exceptions are ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException etc.
- Unchecked Exceptions: The Unchecked Exceptions are called as the Runtime Exceptions because during the Compile-time these exceptions are not caught by the compiler. After compiling, during Runtime, these exceptions like ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, etc., are caught.
How To Work With Exceptions In Java Language?
Now, we hope the Java Exception Definition and Different Types have become clear to you. So, we can now move ahead for the Practical Implementation Process where we will show how to Throw Java Exceptions.
We can throw any Java Exceptions using 3 different processes. Let us check the following section, where we will show the processes that can be used to throw all Checked and Unchecked Exceptions.
1. Using Try-Catch Block:
One of the best methods will be to use the Try-Catch Block. If you assume in the Java Code that there might be any Exception, then you can place the code in the Try Block and define the Exception Name in the Catch Block.
If there is the expected exception, then the Catch Block will execute and end the program normally. If there is no exception, then the Try Block will be executed. Let us check the following code to know more.
Here, we have used the FileNotFoundException from the Checked Exception category to demonstrate.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String fileName = "ZapOne"; // Providing The File Name
File file = new File(fileName); // Creating The File Object
System.out.println("Throw Checked Exception Using Try-Catch Block: ");
System.out.println();
try // Implementing Try Block
{
FileInputStream stream = new FileInputStream(file); // Trying To Access The File
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) // Try-Catch Module
{
System.out.println("Exception Category: "+e); // Exception Type Print
}
}
}
Steps Of The Program:
- At first, the “ZapOne” File will be taken, which doesn’t exist, and its Object will be created.
- Now, in the Try Block, we will try to access the Absent File, which will cause the exception.
- In the Catch Block, we have mentioned the Exception Name, so the Catch Block will be executed.
Output:
2. Using the ” Throw Keyword:
Another way to throw an Exception in Java will be by using the THROW Keyword. The THROW Keyword helps to throw an exception inside of any function or method. This is different from Try-Catch Block.
The THROW Keyword can be utilized to throw exceptions at any point we want. If there is a need to throw an Exception in any Code, then the THROW Keyword will be used to do that deliberately.
Here, we have used the ArithmeticException from the Unchecked Exception category to demonstrate.
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int zap = 40; // Variable Declaration
System.out.println("Throw Unchecked Exception Using THROW Keyword: ");
System.out.println();
if (zap <= 50) // Condition Checking
{
// Implementing Throw Keyword
throw new ArithmeticException("Unsuccessful Due To Low Value");
}
}
}
Steps Of The Program:
- At first, an Integer Variable “Zap” will be created that will have the Value 40.
- Now, we will implement a Conditional Statement that will check whether the Value is less than 50 or not.
- As the Value is less than 50, the Deliberate Exception will be thrown, and the message will be printed.
Output:
3. Using Throws Keyword:
Last but not least, the method will be by using the THROWS Keyword. We have to make a note that the THROW and THROWS keywords are not the same, they are different to use.
The THROWS Keyword is used to avoid unexpected program termination. Using the THROWS Keyword, we can’t get the Exception Message like the Try-Catch Block. It is simply used to bypass the Error.
In the Method Signature in Java, we can declare the pre-assumed exception name to avoid a sudden stop of the program execution. Here, we have used the InterruptedException from the Checked Exception Category.
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException // Implementing Throws To Avoid Exception Message
{
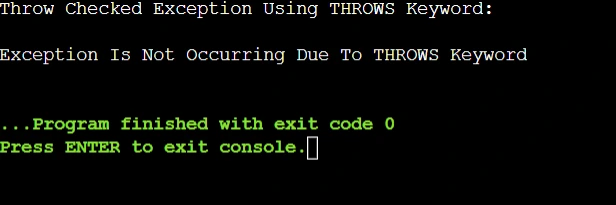
System.out.println("Throw Checked Exception Using THROWS Keyword: ");
System.out.println();
Thread.sleep(100); // Statement That Will Throw An Exception
System.out.println("Exception Is Not Occurring Due To THROWS Keyword"); // Printing A Simple Statement
}
}
Steps Of The Program:
- The Main Function will be implemented where we will throw the InterruptedException.
- In the function, we will use the THREAD Method. If the InterruptedException is not thrown, the THREAD Method will create the Exception and stop the code.
- But as the InterruptedException is thrown, the Exception will be neglected, and the last statement will be printed.
Output:
Comparison Table On Exception Between Java And Other Programming Languages:
The Exception is the concept that is not only present in Java Language, but in all Object-Oriented Programming Languages, we can find similar types of concepts. In this section, we will have a look briefly.
Here, we will make a Comparison Table that will show the difference between the Java Exception and Exceptions in other programming languages like Python and C++.
Criteria | Java Exceptions | Python Exceptions | C++ Exceptions |
Type | Checked | Unchecked | Unchecked |
Handling Type | Strict | Flexible | Flexible |
Syntax | Verbose | Simple | Complex |
Propagation | Explicit | Implicit | Explicit |
Performance | Moderate | Fast | Fast |
What Are Some Real-World Applications Of Throwing Java Exceptions?
Now, if you are thinking that there is no use of Exception Throwing in Java Programming other than for Educational Purposes, then you are thinking wrong. The use of Throwing Exceptions in Java is very long.
From the Web Development to Database Management, in every aspect, the need of Exception Throwing in Java can be seen. In this section, we are going to check some real-world applications of Java Exceptions.
1. Web Applications and API Development:
While working on Web Application and API Development, there might be a chance of having some Runtime issues like Invalid Requests, Authentication Failures, etc. All of these can be solved using Exception Throwing.
When To Use In Real-World Applications:
- In the RESTful APIs, we can handle missing or invalid user input using THROW and THROWS.
- In the Enterprise Web Applications, we can propagate exceptions from Service Layers to Controllers
2. Database Management Systems:
In the field of Database Management Systems or DBMS, the use of Java Exception Throwing can be highly seen to work with different SQL Errors, Connection Failures, and Data Integrity Violations.
When To Use In Real-World Applications:
- If the SQL Query is returning unexpected results, we can throw the Java Exceptions.
- To work on Connection Timeouts and Rollback Transactions, Exception Throwing is needed.
3. Enterprise Software Applications:
As a Java Developer, if we are developing any large-scale Enterprise Applications, then we need to use the Exception Throwing in Java to manage Business Logic Errors, System Faults, etc.
When To Use In Real-World Applications:
- To implement Validation Rules in Financial Applications, we can Throw Exceptions for incorrect data.
- With the Exception Throwing in Java, we can work on Authentication and Authorization Failures.
What Are Some Performance Implications Of Throwing Exceptions In Java?
We hope whatever we have discussed till now will be enough to clear your understanding of Exception Throwing in Java Programming. However, you have to keep in mind some Performance Implications as well.
If you remember these performance implications while practicing the Java Exceptions, there will be a great chance of having a better result. Let us check the following list to know more about.
- When we throw exceptions, it increases the Runtime Overhead due to Stack Trace generation.
- A Code that is Throwing Exception has a Slower Execution Speed than the Normal Code.
- Frequent Exception Throwing can impact the Garbage Collection Algorithm Performance.
- The Memory Consumption of the code will be higher which is throwing some Java Exceptions.
- If we throw Java Exceptions, the optimization of the Java Virtual Machine can be impacted.
What Are Some Common Mistakes On Throwing Exceptions In Java?
As we are approaching towards the end of the discussion, we would like to conclude it by stating some Common Mistakes that most of the student commit while Throwing Exceptions in Java.
Let us check the following list where some of the important Common Mistakes has been discussed that you should take care while writing Java Code on this topic.
- Sometimes, we failed to judge the exception beforehand. That makes the program wrong and cause Unexpected Behaviors. So, we have to assume the exceptions correctly.
- Sometimes, we implement the Try-Catch Syntax in a wrong way that causes another error in the code. So, we have to be careful with syntax.
- Occasionally, we get confused with the THROW and THROWS keywords and place them in improper positions. So, we have to understand their place of use properly.
- Sometimes, in a single Java Program, we use too many exceptions that make the code Complicated and Harder to understand. So, we have to use the exceptions only when there is a need.
- Sometimes, we Throw Exceptions without any kind of Exception Messages. This makes Code Debugging harder in the future. So always, we have to throw exceptions with a message.
Conclusion:
In the end, we can say, understanding “Throw an Exception in Java” is very important to understand.
However we will advise you to clear the Basics of Java Programming before practicing such a complicated Java Topic. If your Basics are clear, then you will find this topic very much simple to understand. If you ever stuck and need help with exception handling in your assignment then you know where you have to go. Reach out to Codingzap and we will take care of your task.
Takeaways:
- To Throw and Exception in Java, we can use Try-Catch, THROW, and THROWS Keywords.
- The THROW and THROWS keywords are not similar thing, they are completely different.
- The Try-Catch Block can be used to Handle Exceptions to avoid unexpected program termination.
- If we want to Manually and Deliberately throw an exception, then the THROW Keyword will be used.
- The THROWS Keyword helps to avoid a certain exception and execute the code in a normal way.